
The Trend of Global Aviation Hubs in Next 20 Years and Its Implications
Fri, Jan 19, 2018
LIANG Zhe, Professor and PhD Supervisor of Tongji SEM
In the next 20 years, the role of the international aviation hub will be more intelligent, more comprehensive and more enriched. The construction of Shanghai international aviation hub focuses on the intelligence of airport, aims at improving the industry of logistics and supply chain, developing an integrated airport economy with a rich connotation. The basis of the construction is a multilevel passenger transport system and a multimode logistics and freight system. It is to create an innovative life atmosphere with interactions of different cultures worldwide and achieve the strategic goal of “One Airport, One City”.
1. Core: An Intelligent Airport
As the core of constructing an international aviation hub, an airport is transforming into an integrated air service provider that focuses on passengers and services. The joint efforts of Artificial Intelligence and Data Science are going to help the airport structure its massive information, and build an interconnected smart Internet of Things (IoT). On this basis, the airport will make comprehensive decisions from a macro perspective, dynamically optimize the allocation of its resources, make timely adjustments and improve operational efficiency of all resources. At the same time, it will be able to provide a broader and more convenient personalized self-service.
1.1 Smart Internet of Things (IoT)
A smart IoT integrates all parts of the airport into an organic whole. For example, based on real-time image information collected by the monitoring network, passenger flow monitor is going to identify, dynamically position and track passengers in the video. The electronic monitoring system will have an auxiliary alarm system to identify suspects and notice security guards when necessary.
Such system will help predict flows in the airport, and in turn trigger an advance alert for possible stranding or crowding situation, so as to ensure sufficient response time for optimal strategies. Passengers’ route information obtained through image recognition techniques can be applied in various aspects in real time.
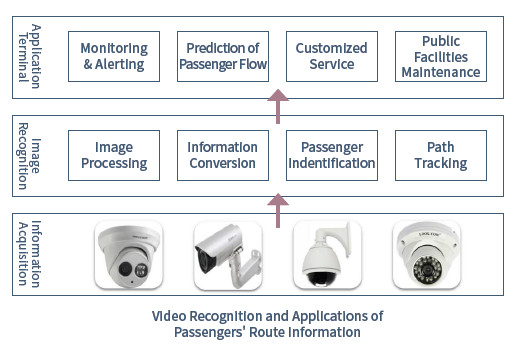
Moreover, pupil and face recognition as well as other AI technologies will be fully used in each step of the auxiliary safety inspection, further compressing labor costs and improving the efficiency of safety check.
1.2 Optimized Allocation of Resources
In order to build an international aviation hub, the construction team is bound to face a more complicated flight flow network as well as a higher demand for throughput of flights, passengers and cargo. Meanwhile, the hub would have to ensure its international competitiveness of services, which requires an even shorter flight connection time and a higher on-time performance rate. In order to achieve the above, the team needs to expand the airport and make layout adjustments, and more importantly, develop a more efficient plan for the allocation of gates and parking stands. The new computer decision support system, different from the old manual one, is going to help the airport fully consider practical factors like passenger utility and flight flow so as to automatically optimize the gate allocation.
A dominant value for passenger-centered and service-oriented airports is a faster security check. For this reason, the airport will have to make better use of attainable data, adjust the opening of security channels on the basis of flow monitoring and forecasting, and send instructional message to passengers through real-time electronic display terminals and information release platforms.
To save passengers’ time, methods will be used to simplify the boarding procedure, examples being e-boarding pass, self-service check-in, self-service baggage check-in and self-service boarding tunnels. Standby airport service workers will be dispatched to other positions, improving the service quality and fully optimizing consumers’ experience.
1.3 Efficient Layout and Maintenance of Public Facilities
Based on the historical data of passenger flow changes, the airport has to evaluate regular or irregular changes in function plan of interior areas and public facility layout. Rentals for shops and advertisements will be further quantified, and rest areas and water fountains will be better located.
Based on the real-time data analysis of passenger flows, adjustments will be made in frequency of toilet cleaning and replenishment of free supplies, so as to achieve a positive correlation between the usage, damage of public facilities and the maintenance frequency.
1.4 Real-time Service and Network Interaction
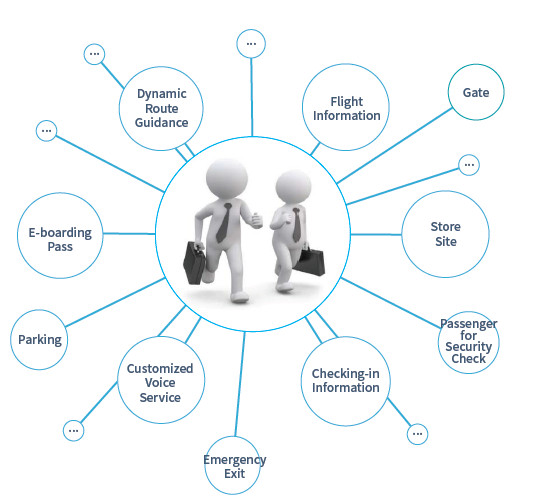
Based on the application data provided by the smart IoT, passengers’ needs for information will be satisfied to the greatest extent through their mobile terminals as well as electronic display devices in the airport. Information that they will obtain in real time includes flight status, e-boarding pass, gate number, and passenger flow in the security check. Moreover, with such technology, passengers could check in, register their luggage and even board through self-service.
Terminals of the smart IoT will not only collect information about passengers’ real-time position and movement, but also provide more personalized navigation services, including electronic navigation marks on the ground and corresponding voice prompts in their ears. Additionally, synchronous prompt messages on passengers’ private mobile terminals would recommend dinning and shopping activities based on their preferences. The larger but more refined application of data science will help the airport to provide a more punctual and high-quality service.
2. An Integrated Airport Economy
On the second Yangtze River Development Forum in this August, Wang Xuedong, Director of International Aerotropolis Research Center of Fudan University, released the Development Report of China’s Airport Economic Zone (Aerotropolis) and the Development Index Report of the Airport Economic Zone (Aerotropolis) Among the Yangtze River Economic Belt. According to public information and sample assessment, the reports scored and ranked 27 airport economic zones in the country as well as 9 airport economic zones among the Yangtze River economic belt. The top three in comprehensive competitive power are the airport economic zones of Shanghai, Beijing and Guangzhou.
For the development of an airport economic zone, the hub airport is the core and carrier, while the comprehensive transportation system being an important support. The development of industries in surrounding areas attracted to and radiated by the airport is reflected by the airport economy. The hinterland economy is mainly shown by the abundant sources of passengers and cargo provided by city economy, business economy, tourism economy, foreign trade development and so on. As can be seen, the comprehensive competitive power of Shanghai Airport Economic Zone has an absolute advantage.
The development of airport economy can be traced back to Ireland’s Shannon International Airport Free Trade Zone in 1959, of which the practice of top-level design from a global perspective provides reference for the construction of Shanghai’s aviation hub. A service-oriented airport has the power to significantly improve the transfer rate, reduce the proportion of irregular flights and strengthen the flight flow network. Logistic and supply chain, high-tech manufacturing and other airport-related industries will gradually integrate to finally form an industrial cluster. Abundant supply of passengers and cargo provides a healthy environment for the development of airport service industry. With the support of abundant seaport freight and the airport, Shanghai’s airport economy will surely bring an extremely strong regional radiation power, and thus help bring forth a stable and integrated airport economic zone.
2.1 Early Stage: Improving Basic Transportation Functions
According to the Statistical Communique on Development of Civil Aviation Airports released by Civil Aviation Administration of China, from the year 2010 to 2016, the combined passenger and cargo throughput of airports in Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou accounted for nearly half of the total throughput within China. The above statistical communique of the year 2016 shows that the passenger and cargo throughput of civil aviation airports in Shanghai ranked first in the country and had been steadily increasing in the recent five years. The ranking of passenger throughput of Pudong Airport among domestic civil aviation airports had been climbing year by year, with its cargo and mail throughput ranking first in China.
Shanghai aviation hub is constructed from the perspective of global cities. With the advantage of the two airports, Pudong and Hongqiao, it aims to form an airport economic circle with two reciprocal centers. In this case, the premise would be to efficiently improve and steadily increase the airports’ throughput of both passenger and cargo. Centered on the intelligent two-airport core areas, authorities need to make compact plans of metro, improve the traffic efficiency within the city, strengthen Shanghai’s connection with its satellite cities, integrate intercity high-speed railway with urban rail transit, therefore forming a multidimensional traffic network. Pudong and Hongqiao will become two intersectional hubs of three kinds of traffic networks from different dimensions, namely, urban transport, nationwide rail traffic and international air traffic.
2.2 Fusion Stage: A Combinatorial Logistics Distribution Industry
Airport logistics is characterized by its fast speed, large-span delivery area, easy access, freshness of goods, accuracy, convenience and high security. Located near the global route and at the edge of the global sea route, the port of Shanghai has a convenient land and water transportation as well as an unobstructed channel for consolidation and distribution. It is able to access the whole country through the expressways, national highways, rail lines and costal shipping network.
The comprehensive industry of both airport and maritime logistics will go through a phase of planning, intensification, highly informatization and process visualization. With the support of the big data system of smart logistics, the transformation and upgrading of the logistic industry is going to achieve an economy of scale, and then an economy of velocity with the advantage of time efficiency.
2.3 Maturing Stage: The Generation of Innovative Service Industries
With a scaled-up airport area and a higher operational efficiency, passengers would have more free time for shopping and leisure, requiring a better indoor planning. The integrated hub of aviation, high-speed rail and metro will provide a large number of effective potential customers and an excellent living environment for the tertiary industry.
Further on, the airport industry within 6-20km of the airport will form a comprehensive open system connected to major cities worldwide through the global route network. The system is going to be abundant in all kinds of economic factors like funds, information, technology and talents. Therefore, it would be able to quickly integrate into the global economic network, to speed up the circulation of the economic system and to promote the interconnection of global markets. As an international aviation hub, Shanghai hub is going to gradually reveal its free trade function, promptly responding to consumer demand for medium to high-end goods around the world.
2.4 Stable Stage: A Sustainable Boost for the Regional Economy
Up to now, Shanghai has already constructed the Hongqiao Linkong Business Park, its planned area being 5.14km². It is located in the west of Changning District, adjacent to the world’s largest Hongqiao Integrated Transport Hub. With a development goal of being high-profile, “garden-style, high-tech and headquarters-type”, coupled with the advantage in transportation, the business park has become the most dynamic and influential modern service industry cluster connecting the Pan-Yangtze River Delta and the Yangtze River Basin.

Hongqiao Linkong Business Park is a good start of the construction of Shanghai aviation hub from the perspective of global city of excellence. Better economic benefits and regional radiation power will be achieved by Pudong-Hongqiao dual-airport center and the coexistence of three ports–the port of Shanghai, Pudong and Hongqiao airports. What are to be planned and constructed in the park include logistics and supply industry park, high-tech manufacturing industry base, comprehensive bonded zone, high-end business zone, shopping and leisure area. On this basis, industry clusters would be formed such as logistics distribution, logistics transfer, bonded warehousing, international procurement, process and export, in order to promote coordinated development of three industries and thus form an integrated airport economic area with sustainable radiation capability.
3. A Globalized Aerotropolis
According to the Fiscal Year 2016 Interim Report issued by Hong Kong International Airport, the incomes of three businesses other than shipping, namely, franchises, retail licenses and advertising, and business revenues of other terminals accounted for 64.1% of the total revenue during the reporting period. This shows that the economic benefits of businesses attached to the airport are quite impressive.
In February 2017, Civil Aviation Administration of China, National Development and Reform Commission and the Ministry of Transport jointly issued The 13th Five-Year Plan for the Development of China’s Civil Aviation. It was proposed in the report that, during the 13th FYP period, China will build and continue to build 74 new airports in total, with the completion of 50 airports. By 2020, the number of civil transport airports in China will have grown to more than 260 from 207 in 2015. In other words, China’s aviation industry will continue to expand. More economic and social benefits will be achieved by Shanghai – the aerotropolis housing two major aviation hubs.
According to Shanghai’s urban development planning, the next two decades will be the historical stage for Shanghai to join the global cities from a higher starting point. The development goal of urban comprehensive transport is to build a “low carbon, accessible” comprehensive transport system. In the 13th FYP period, relying on “Big Hongqiao Strategy” and “Big Pudong Strategy”, Shanghai is going to form an urban pattern of dual engines — Hongqiao in the west and Pudong in the east. Under the background of an interconnected multilevel passenger transport and an integrated multimode freight logistics, a large amount of airport industries will gather around the airport with their advantage of location and enrichment function of economic elements. An aerotropolis space with harmonious economic and social sociology will in turn come into being under the symbiosis effect of these airport industries.
3.1 A Multilevel and Interconnected Transportation
From the macroscopic view of major global cities, it is significant for Shanghai, an international mega-city, to have a comprehensive transportation network. Powerful airports and ports will be responsible for frequent interactions of economy and trade between the city and the world. A highly efficient and wide-coverage network of high-speed railway and expressway is going to help establish the city’s core status in the regional city group. A dense and comfortable urban transportation network is to shoulder the responsibility of ensuring citizens’ everyday social life and work.
Furthermore, from the perspective of global cities, airports, especially their transportation, have to be more intelligent, comprehensive, and connotative. The networks of international aviation, domestic railway, inter-city high-speed railway, urban rail and urban non-motorized traffic all gathered at the airport in order to transfer and transit passengers and cargo. In the future, the basic characteristic of a global aerotropolis will be the concentration ability of an automated multilevel and interconnected transportation network.
3.2 A Multimode Supply Chain System
A multilevel and interconnected transportation network, with its gathering core being the airport, aims to build a solid foundation for the establishment of a mature logistics supply chain system and an airport logistics park. The airport logistics park is going to cover all aspects of the logistics service industry: distribution and processing, packaging, transit, distribution, warehousing and transportation. High-tech industry parks near the airport are going to bring together aerospace-related industries like high-end manufacturing and light processing. High-tech industrial bases around the airport will provide a good living space for the development and manufacturing of microelectronics and computers which rely heavily on air transport. Industries of logistics distribution and high-end manufacturing gather closely around industry clusters near the airport, so as to achieve seamless connection with the international supply chain and to improve their service response level.
3.3 An Innovative Multicultural Life
With the airport being the core, and the airport-oriented industry as the background, the aerotropolis is going to define an innovative lifestyle: a multilevel and interconnected transportation network, a global shopping mall, international integrated business modules, cultural collision and integration brought about by high-efficient flow of passengers and cargo. An aerotropolis, created on the basis of Shanghai aviation hubs, will surly deliver a high-quality urban experience with excellent infrastructure and perfect software. Moreover, apart from standardized infrastructure, Shanghai’s inclusiveness of different cultures worldwide will be reflected in its urban style as an aerotropolis.
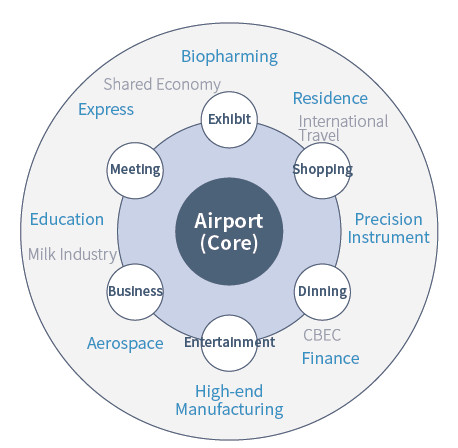
A General View of an Aerotropolis
We protect your privacy. We use cookies to personalize content, provide features, and analyze traffic to our website anonymously and in a privacy compliant manner. By law, we may store cookies on your device if they are strictly necessary for the operation of this site. For all other cookie types, we need your permission. For more information, please see the privacy policy linked below.